Description
Basic Parameters
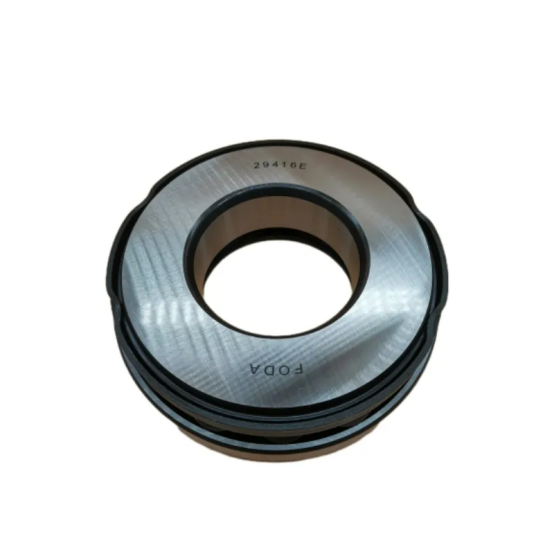
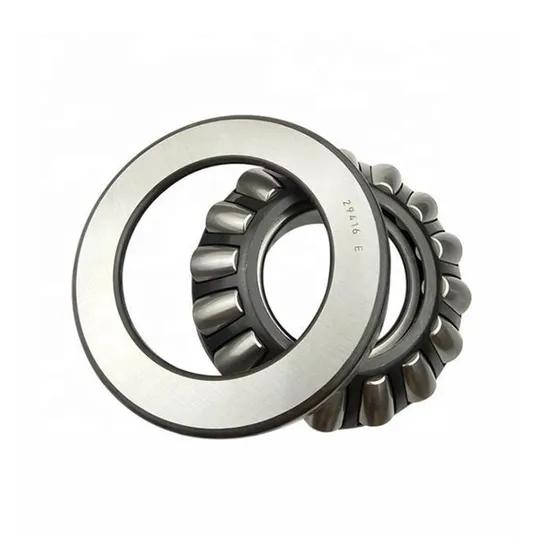
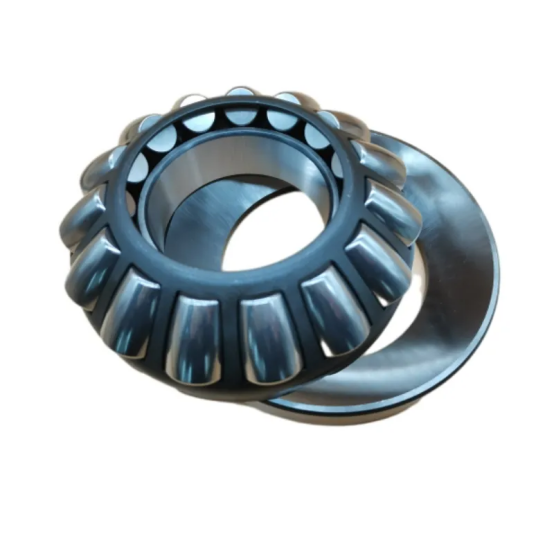
Here is the basic parameter of the thrust roller bearing with the specific model 29416E. The inner diameter of this bearing is 80 mm, the outer diameter is 170 mm, and the width is 58 mm. It has a rated dynamic load of 985 kN and a rated static load of 2300 kN, with a limit speed of 1200 r/min. Weighing approximately 6.2 kg, it is made of high-carbon chromium bearing steel (GCr15), suitable for grease or oil lubrication. With a standard radial clearance (customizable), it can work in the temperature range of -30°C to +120°C. As a thrust aligning roller bearing, it is widely applied in heavy machinery, metallurgical equipment, mining machinery, etc., featuring strong axial load capacity, good rigidity, low friction coefficient and strong impact resistance.
Characteristics
1.Large bearing capacity: can withstand large axial load.
2. Good rigidity: When bearing axial force, it is not easy to produce deformation.
3. Low friction coefficient: relatively smooth operation, reduce energy loss.
4. Strong impact resistance: able to withstand a certain degree of impact load.
The Working Principle
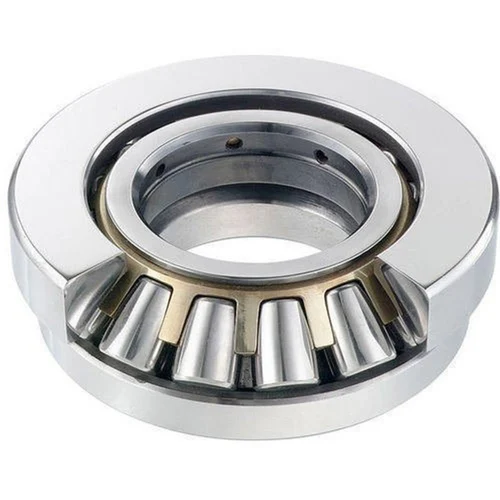
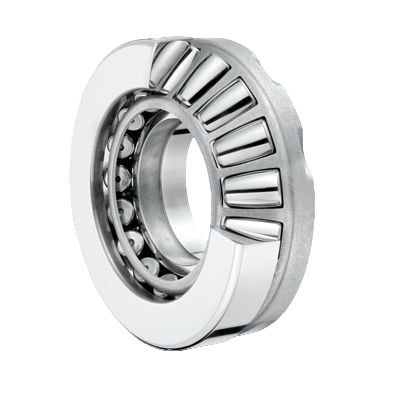
1. Core Structural Components
Rollers: Cylindrical, tapered, or spherical in shape (depending on the bearing type), these are the key load-transmitting elements.
Raceways: Comprise a shaft ring (attached to the rotating shaft) and a seat ring (fixed to the housing or support structure). The rollers roll between these two rings.
Cage: Guides and spaces the rollers to prevent direct contact and ensure uniform load distribution.
2. Load Transmission Mechanism
When an axial load (force along the shaft’s axis) is applied to the shaft, the load is transferred to the shaft ring.
The rollers then roll along the raceways of the shaft ring and seat ring, converting sliding friction (which generates more heat and wear) into rolling friction (much lower resistance).
This rolling motion allows the bearing to efficiently transmit the axial load from the shaft to the housing or support structure, maintaining the shaft’s rotational stability.
3. Self-Adjustment (for Aligning Types)
In thrust aligning roller bearings, the spherical shape of the rollers or raceways enables automatic alignment with shaft misalignment or slight tilting. This feature compensates for angular errors, preventing premature wear and ensuring smooth operation even under off-axis loads.
4. Key Advantages in Operation
Low Friction: The rolling motion of the rollers reduces energy consumption, making the bearing suitable for high-efficiency applications.
High Rigidity: Stiff structural design minimizes deformation under heavy axial loads, ensuring precise shaft positioning.
Impact Resistance: Robust roller and raceway materials (e.g., high-carbon steel) enable the bearing to withstand sudden impact loads without failure.
5. Typical Working Scenario
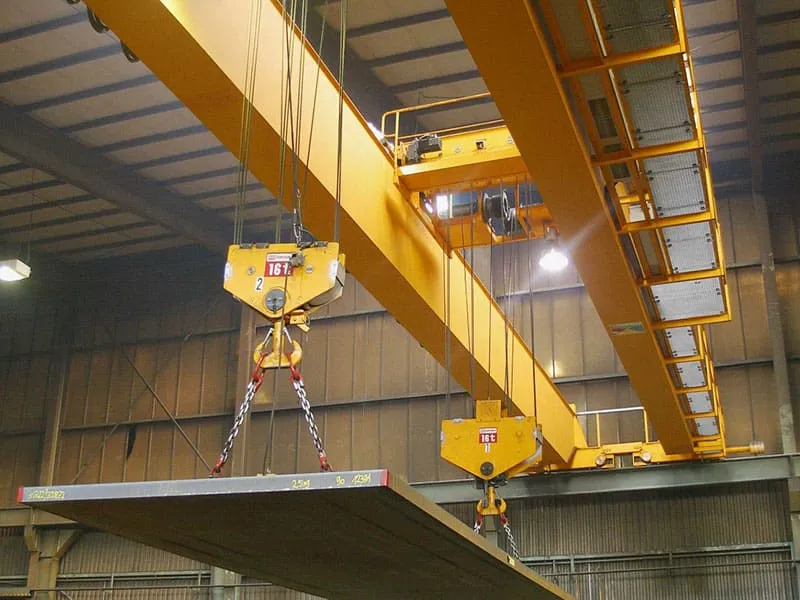
Example: In a crane’s hoisting mechanism, when the shaft experiences upward or downward axial forces from lifting loads, the thrust roller bearing’s rollers roll between the shaft and seat rings, channeling the load to the crane’s frame. This allows the shaft to rotate smoothly while supporting the heavy load, demonstrating the bearing’s core function of axial load management through rolling contact.
Application Fields
Heavy Machinery: Deployed in cranes, excavators, and large construction equipment to withstand massive axial forces generated during lifting, digging, and rotational operations.
Metallurgical Equipment: Integrated into rolling mills, continuous casting machines, and steel processing lines to ensure stable shaft operation under heavy loads and high-temperature conditions.
Mining Machinery: Used in crushers, vibrating screens, and conveyor systems in mining sites, providing robust support against abrasive dust, shocks, and continuous heavy-duty operation.
Power Generation: Installed in steam turbines, generators, and hydroelectric equipment to manage axial thrust from rotating shafts while accommodating slight misalignments in high-speed applications.
Industrial Gearboxes: Applied in marine gearboxes, cement mill reducers, and heavy-duty transmission systems, where its self-aligning capability and low friction coefficient enhance operational efficiency and reduce maintenance costs.
Product List









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.