Description
Basic Parameters
Diameter: Common diameter specifications range from a few millimeters to tens of millimeters.
Hardness: Generally between HRC60-66.
Accuracy level: As mentioned above, different levels correspond to different accuracy requirements.
Surface roughness: usually in microns, the higher the grade, the smaller the surface roughness.
Material composition: mainly contains carbon, chromium, manganese, silicon and other elements, the composition ratio of different materials will be different.
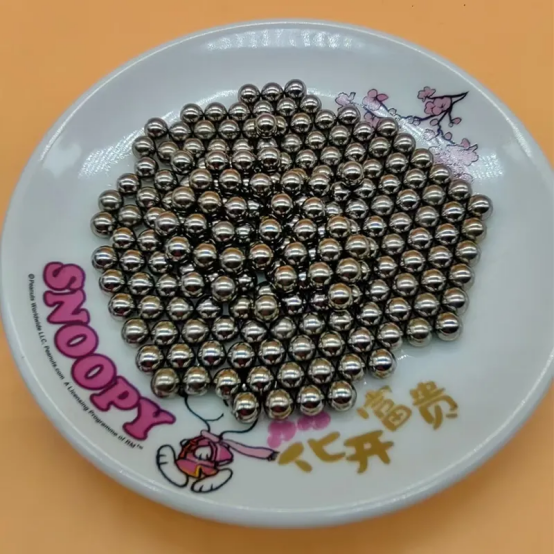
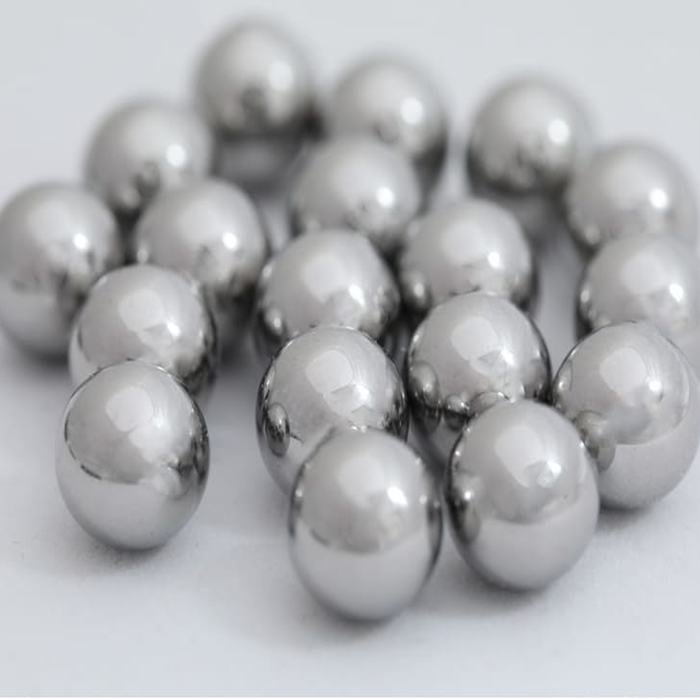
Bearing Steel Balls feature high-carbon chromium steel (e.g., GCr15, AISI 52100), stainless steel (SS440C), or ceramic (Si3N4), with diameters ranging from 1 mm to 100 mm (custom sizes available). Engineered for precision, they meet ABEC-1 to ABEC-9 or ISO Grade 10 to 1000 standards, boasting hardness levels of 60–65 HRC for GCr15 steel, 58–62 HRC for stainless steel, and ≥80 HRC for ceramic. Polished to a surface roughness of 0.01–0.1 μm with optional anti-rust coatings, they offer diameter tolerances of ±0.001–0.01 mm and roundness ≤0.002 mm for high-precision grades. Suitable for automotive bearings, electric motors, aerospace, and industrial machinery, they comply with ISO 3290, ABEC, or custom specifications.
Characteristics
High precision: It has strict dimensional accuracy and roundness to ensure smooth running of bearings.
High hardness: can withstand greater pressure and friction, not easy to deformation and wear.
Good wear resistance: During long-term use, it can maintain good surface quality and extend the service life of bearings.
Good stability: stable and reliable performance in different working environments.
Bearing Steel Balls are engineered for precision and durability, offering exceptional load-bearing capacity and low friction for smooth mechanical motion. Crafted from high-grade materials like GCr15 (AISI 52100) bearing steel, stainless steel (e.g., SS440C), or ceramic (Si₃N₄), they feature superior hardness (60–65 HRC for steel, ≥80 HRC for ceramic) and resistance to wear, corrosion, and high temperatures. Polished to mirror-like surfaces (Ra 0.01–0.1 μm) with tight dimensional tolerances (±0.001–0.01 mm) and roundness precision (≤0.002 mm for high grades), these balls meet strict ABEC/ISO standards (Grade 10 to 1000) for consistent performance. Available in diameters from 1 mm to 100 mm (custom sizes optional), they offer versatile solutions for automotive, aerospace, industrial machinery, robotics, and precision instruments, with optional anti-rust coatings (black oxide, chrome plating) to enhance longevity in harsh environments. Their uniform structure and heat-treated integrity ensure minimal deformation under heavy loads, making them critical components for reliable rotational systems.
Material
1. High-Carbon Chromium Bearing Steel
Grade Examples: GCr15 (China), AISI 52100 (US), SUJ2 (Japan)
Composition: 1.0% carbon, 1.5% chromium, balanced iron with trace elements (manganese, silicon)
Key Properties:
Hardness: 60–65 HRC, ensuring high wear resistance and load capacity
Microstructure: Fine martensite after quenching, minimizing deformation under stress
Fatigue Strength: Ideal for high-speed, heavy-load applications (e.g., automotive transmissions, industrial motors)
Standards: Compliant with ISO 683-17, AISI 52100, or JIS SUJ2.
2. Stainless Steel
Grade Examples: SS440C, 440B, 316
Composition: 16–18% chromium, 0.7–1.2% carbon (440C), with nickel/molybdenum in 316 grade
Key Properties:
Hardness: 58–62 HRC (440C), combining corrosion resistance with mechanical strength
Resistance: Excellent against moisture, chemicals, and high-temperature oxidation
Applications: Medical devices, food processing, marine equipment, and harsh environments.
3. Ceramic Materials
Grade Examples: Silicon Nitride (Si₃N₄), Zirconia (ZrO₂)
Key Properties:
Hardness: ≥80 HRC (Si₃N₄), far exceeding steel for wear resistance
Low Density: 60% lighter than steel, reducing centrifugal forces in high-speed applications
Thermal & Electrical Insulation: Suitable for high-temperature (up to 1200°C) and electrically isolated systems
Applications: Aerospace bearings, semiconductor machinery, and precision instruments.
4. Heat Treatment & Surface Enhancement
Processes:
Vacuum quenching and tempering to optimize toughness and hardness
Surface treatments: Black oxide, chrome plating, or PTFE coating for anti-rust and low-friction needs
Purpose: Enhances fatigue life, reduces friction, and extends service life in corrosive environments.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.