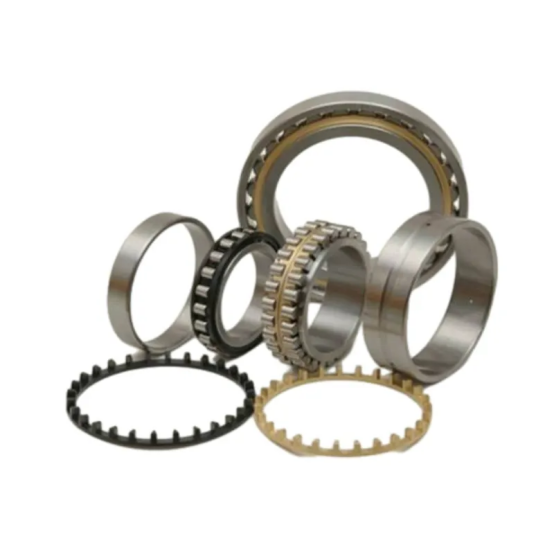
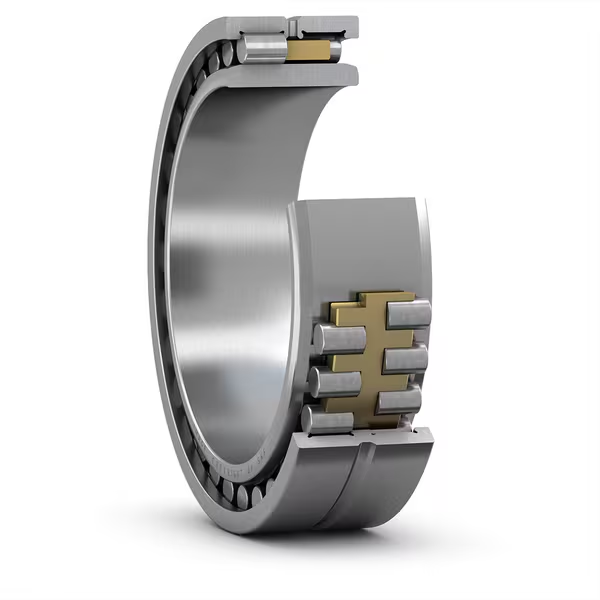
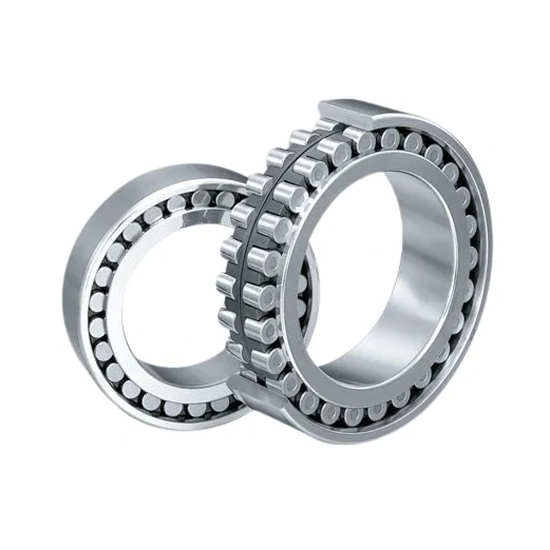
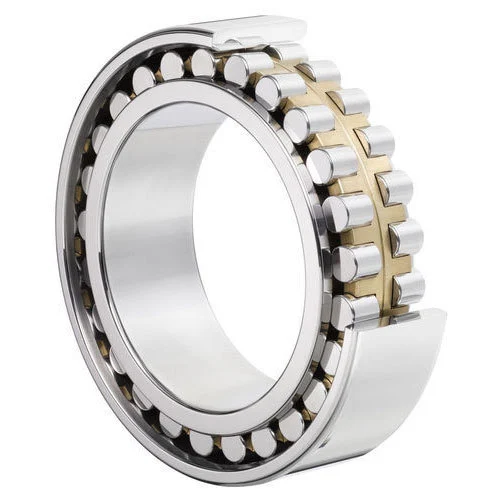
Description
Basic Parameters
Super Precision Roller Bearings are engineered for applications requiring high rigidity, exceptional load capacity, and outstanding rotational accuracy. These bearings are typically designed to accommodate heavy radial loads and moderate axial loads, making them ideal for high-speed and high-precision environments. Key parameters include:
Bearing Type: Cylindrical Roller Bearings or Tapered Roller Bearings (depending on application)
Precision Class: ISO P4, P2 or equivalent JIS Class 4/2, ensuring ultra-tight dimensional tolerances
Contact Geometry: Optimized roller and raceway profile for reduced stress concentration and improved load distribution
Load Capacity: High radial load capacity with enhanced axial load support in double-row or paired configurations
Rigidity: High internal stiffness, crucial for resisting deformation in machine tool spindles and precision equipment
Speed Capability: Suitable for high-speed operation, with low vibration and stable running performance
Material: High-quality bearing steel (e.g., SUJ2), with optional hybrid designs using ceramic rollers for reduced friction and heat generation
Cage Options: Precision-machined brass, phenolic resin, or polyamide cages for improved durability and high-speed stability
Lubrication: Available with grease or oil lubrication systems, including provisions for high-speed oil-air lubrication
Configuration: Single row, double row, or custom-matched bearing sets depending on load direction and application needs
Applications: Widely used in grinding machines, turning centers, high-speed spindles, aerospace tooling, and precision robotics
These parameters ensure that Super Precision Roller Bearings deliver superior performance in demanding applications that require both load-bearing strength and motion accuracy.
Product Application
1. High-Precision Industrial Machinery
CNC Machines
Used in spindle and feed systems to ensure micron-level positioning accuracy, reducing machining errors and improving surface finish and dimensional consistency for precision parts (e.g., aerospace components, optical elements).
Precision Gearboxes
Supports high-speed gear transmission, minimizes meshing vibration and noise, and ensures transmission efficiency and stability in robots and automated production lines.
2. Aerospace & Defense
Aircraft Engines
Provides reliable support for high-temperature and high-speed components like turbine rotors and compressors, withstanding high loads and alternating stresses to meet aviation-grade fatigue resistance and long-life requirements.
Missile Guidance Systems
Ensures high-precision rotation of inertial navigation devices, reduces vibration interference, and enhances the stability of missile trajectory control.
3. Precision Instruments & Measuring Equipment
Coordinate Measuring Machines (CMM)
Supports the high-precision movement of measuring arms, preventing mechanical errors that affect millimeter-to-micron-level dimensional inspection accuracy.
Optical Telescopes/Microscopes
Used in focusing mechanisms and rotating platforms for gap-free, low-friction motion, ensuring stability in astronomical observation or cellular microscopy.
4. Semiconductor & Electronics Manufacturing
Wafer Fabrication Tools
Supports wafer rotating tables in lithography machines and ion implanters, ensuring nano-level positioning and rotation to avoid defects in semiconductor chip production.
Hard Disk Drives (HDD)
Supports high-speed, precise movement of read/write heads, reducing seek errors and enhancing data read/write reliability and speed.
5. Medical Equipment
Surgical Robots
Used in robotic arm joints to achieve sub-millimeter precise motion control, meeting the high-precision requirements of minimally invasive surgeries (e.g., prostatectomy, heart bypass).
Medical Imaging Devices (MRI/CT Scanners)
Supports rotating frames and detector arrays, reducing vibration noise to ensure clarity and diagnostic accuracy in tomographic images.









Reviews
There are no reviews yet.